CSVLayer
require(["esri/layers/CSVLayer"], function(CSVLayer) { /* code goes here */ });esri/layers/CSVLayerThe CSVLayer is a point layer based on a CSV file (.csv, .txt). CSV is a plain-text file format used to represent tabular data, including geographic point features (latitude, longitude). Typically the latitude coordinate is the Y value, and the longitude coordinate is the X value. Features from the CSV file are accessible via the API so you can query features and use them as input to geometry or geoprocessing services.
If CSV files are not on the same domain as your website, a CORS enabled server or a proxy is required. The following snippet shows how to add a new CSVLayer instance to a map.
var url = "https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/2.5_week.csv";
var csvLayer = new CSVLayer({
url: url,
copyright: "USGS Earthquakes"
});
map.add(csvLayer); // adds the layer to the map
- See also:
Constructors
- new CSVLayer(properties)
- Parameter:properties Objectoptional
See the properties for a list of all the properties that may be passed into the constructor.
Example:// Typical usage var layer = new CSVLayer({ // URL to the CSV file url: "https://mydomain.com/files/POIs.csv" });
Property Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| String | Copyright information for the layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | The name of the class. more details | more details | Accessor | |
| String | The SQL where clause used to filter features on the client. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | The column delimiter. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Object | Specifies how graphics are placed on the vertical axis (z). more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Object | Configures the method for decluttering overlapping features in the view. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Field[] | An array of fields in the layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Extent | The full extent of the layer. more details | more details | Layer | |
| String | The unique ID assigned to the layer. more details | more details | Layer | |
| LabelClass[] | The label definition for this layer, specified as an array of LabelClass. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether to display labels for this layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | The latitude field name. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether the layer will be included in the legend. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | Indicates how the layer should display in the LayerList widget. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether the layer's resources have loaded. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Error | The Error object returned if an error occurred while loading. more details | more details | Layer | |
| String | Represents the status of a load operation. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Object[] | A list of warnings which occurred while loading. more details | more details | Layer | |
| String | The longitude field name. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Number | The maximum scale (most zoomed in) at which the layer is visible in the view. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Number | The minimum scale (most zoomed out) at which the layer is visible in the view. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Number | The opacity of the layer. more details | more details | Layer | |
| String[] | An array of field names to include in the CSVLayer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether to display popups when features in the layer are clicked. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| PopupTemplate | The popup template for the layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Renderer | The renderer assigned to the layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Boolean | Apply perspective scaling to screen-size point symbols in a SceneView. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| SpatialReference | The spatial reference of the layer. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | The title of the layer used to identify it in places such as the Legend and LayerList widgets. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | For CSVLayer the type is | more details | CSVLayer | |
| String | The URL of the CSV file. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Boolean | Indicates if the layer is visible in the View. more details | more details | Layer |
Property Details
- copyrightString
Copyright information for the layer.
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
The name of the class. The declared class name is formatted as
esri.folder.className.
- definitionExpressionStringSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
The SQL where clause used to filter features on the client. Only the features that satisfy the definition expression are displayed in the View. Setting a definition expression is useful when the dataset is large and you don't want to bring all features to the client for analysis. Definition expressions may be set when a layer is constructed prior to it loading in the view or after it has been added to the map. If the definition expression is set after the layer has been added to the map, the view will automatically refresh itself to display the features that satisfy the new definition expression.
Examples:// Set definition expression in constructor to only display earthquakes magnitude 5.0 and greater const layer = new CSVLayer({ url: "https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/2.5_week.csv" definitionExpression: "mag >= 5" });// Set the definition expression directly on layer instance after it has loaded layer.definitionExpression = "mag >= 5";
- delimiterString
The column delimiter. See the table below for possible values.
Value Description ,comma space ;semicolon |pipe \ttab-delimited
- elevationInfoObject
Specifies how graphics are placed on the vertical axis (z). This property may only be used in a SceneView. See the ElevationInfo sample for an example of how this property may be used.
- Properties:
- mode String
Defines how the graphic is placed with respect to the terrain surface. See the table below for a list of possible values.
Mode Description on-the-ground Graphics are draped on the terrain surface. This is the default value for Point geometries rendered with ObjectSymbol3DLayers. relative-to-ground Graphics are placed at an elevation relative to the terrain surface. The graphic's elevation is determined by summing up the terrain elevation and the result of featureExpressionInfo(if defined). This is the default value for Point geometries rendered with IconSymbol3DLayers.absolute-height Graphics are placed at an absolute height above sea level. This height is determined by the result of featureExpressionInfo(if defined). This mode doesn't take the elevation of the terrain into account.relative-to-scene Graphics are aligned to buildings and other objects part of 3D Object SceneLayers or IntegratedMeshLayers, depending on which has higher elevation. If the graphic is not directly above a building or any other feature, it is aligned to the terrain surface elevation. If defined, the result of featureExpressionInfois added to the 3D Object/terrain surface elevation.optionaloffset NumberAn elevation offset, which is added to the vertical position of the graphic. If
unitis not defined, the offset is inmeters. Whenmode = "on-the-ground", this property has no effect.optionalfeatureExpressionInfo ObjectThis object contains information about setting a custom height on the graphic. If this property is set, then z values are not considered for calculating graphic height.
- Specification:
- optionalexpression String
An Arcade expression evaluating to a number that determines the height of the graphic. When
mode = "on-the-ground", this property has no effect. For line and polygon geometries the result of the expression is the same for all vertices of a feature.
optionalunit StringThe unit for
featureExpressionInfoandoffsetvalues.Possible Values: feet | meters | kilometers | miles | us-feet | yards
- featureReductionObjectSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.4
Configures the method for decluttering overlapping features in the view. If this property is not set (or set to
null), every feature is drawn individually.Currently this property is only supported in 3D SceneViews for point features with non-draped Icons or Text symbol layers.
- Property:
- type String
Type of the decluttering method. The only supported type at the moment is
selection. In this method, some of the overlapping features are hidden such that none of the remaining features intersect on screen. Label deconfliction also respects this option and hides labels that would overlap with the features of this layer. - See also:
Example:layer.featureReduction = { type: "selection" };
- fieldsField[]
An array of fields in the layer.
Example:// define each field's schema var fields = [ new Field({ "name": "ObjectID", "alias": "ObjectID", "type": "oid" }), new Field({ "name": "description", "alias": "Description", "type": "string" }), new Field ({ "name": "title", "alias": "Title", "type": "string" }) ];
The full extent of the layer. By default, this is worldwide. This property may be used to set the extent of the view to match a layer's extent so that its features appear to fill the view. See the sample snippet below.
Example:// Once the layer loads, set the view's extent to the layer's fullextent layer.when(function(){ view.extent = layer.fullExtent; });
The unique ID assigned to the layer. If not set by the developer, it is automatically generated when the layer is loaded.
- labelingInfoLabelClass[]autocastAutocasts from Object[]
The label definition for this layer, specified as an array of LabelClass. Use this property to specify labeling properties for the layer.
For labels to display in the view, the labelsVisible property of this layer must be set to
true.Multiple Label classes with different
whereclauses can be used to define several labels with varying styles on the same feature. Likewise, multiple label classes may be used to label different types of features (for example blue labels for lakes and green labels for parks).Known Limitations
Currently only one LabelClass is supported in 3D SceneViews.
- See also:
Example:const statesLabelClass = new LabelClass({ labelExpressionInfo: { expression: "$feature.NAME" }, symbol: { type: "text", // autocasts as new TextSymbol() color: "black", haloSize: 1, haloColor: "white" } }); csvLayer.labelingInfo = [ statesLabelClass ];
- labelsVisibleBoolean
Indicates whether to display labels for this layer. If
true, labels will appear as defined in the labelingInfo property.Known Limitations
- Currently only one LabelClass is supported in 3D SceneViews.
- Currently the
labelsVisibleproperty must be explicitly set totruefor labels to be printed.
- Default Value:true
- See also:
- latitudeFieldString
The latitude field name. If not specified, the API will look for following field names in the CSV source: "lat", "latitude", "y", "ycenter", "latitude83", "latdecdeg", "POINT-Y".
- legendEnabledBoolean
Indicates whether the layer will be included in the legend.
- Default Value:true
Indicates how the layer should display in the LayerList widget. The possible values are listed below.
Value Description show The layer is visible in the table of contents. hide The layer is hidden in the table of contents. hide-children If the layer is a GroupLayer, hide the children layers from the table of contents. - Default Value:show
Indicates whether the layer's resources have loaded. When
true, all the properties of the object can be accessed.- Default Value:false
The Error object returned if an error occurred while loading.
- Default Value:null
Represents the status of a load operation.
Value Description not-loaded The object's resources have not loaded. loading The object's resources are currently loading. loaded The object's resources have loaded without errors. failed The object's resources failed to load. See loadError for more details. - Default Value:not-loaded
A list of warnings which occurred while loading.
- longitudeFieldString
The longitude field name. If not specified, the API will look for following field names in the CSV source: "lon", "lng", "long", "longitude", "x", "xcenter", "longitude83", "longdecdeg", "POINT-X".
- maxScaleNumber
The maximum scale (most zoomed in) at which the layer is visible in the view. If the map is zoomed in beyond this scale, the layer will not be visible. A value of
0means the layer does not have a maximum scale. The maxScale value should always be smaller than the minScale value.- Default Value:0
Examples:// The layer will not be visible when the // view is zoomed in beyond a scale of 1:1,000 layer.maxScale = 1000;// The layer's visibility is not restricted to a maximum scale. layer.maxScale = 0;
- minScaleNumber
The minimum scale (most zoomed out) at which the layer is visible in the view. If the map is zoomed out beyond this scale, the layer will not be visible. A value of
0means the layer does not have a minimum scale. The minScale value should always be larger than the maxScale value.- Default Value:0
Examples:// The layer will not be visible when the view // is zoomed out beyond a scale of 1:3,000,000 layer.minScale = 3000000;// The layer's visibility is not restricted to a minimum scale. layer.minScale = 0;
The opacity of the layer. This value can range between
1and0, where0is 100 percent transparent and1is completely opaque.- Default Value:1
Example:// Makes the layer 50% transparent layer.opacity = 0.5;
- outFieldsString[]
An array of field names to include in the CSVLayer. If not specified, the layer will include all fields.
Examples:// Use all fields (the default) layer.outFields = ["*"];// Use a subset of fields layer.outFields = ["NAME", "POP_2016", "FIPS"];
- popupEnabledBoolean
Indicates whether to display popups when features in the layer are clicked.
- Default Value:true
- popupTemplatePopupTemplateautocast
The popup template for the layer. When set on the layer, the
popupTemplateallows users to access attributes and display their values in the view's popup when a feature is selected using text and/or charts. See the PopupTemplate sample for an example of how PopupTemplate interacts with a FeatureLayer.
The renderer assigned to the layer. The renderer defines how to visualize each feature in the layer. Depending on the renderer type, features may be visualized with the same symbol, or with varying symbols based on the values of provided attribute fields or functions.
- See also:
Example:// all features in the layer will be visualized with // a 6pt black marker symbol and a thin, white outline layer.renderer = { type: "simple", // autocasts as new SimpleRenderer() symbol: { type: "simple-marker", // autocasts as new SimpleMarkerSymbol() size: 6, color: "black", outline: { // autocasts as new SimpleLineSymbol() width: 0.5, color: "white" } } };
- screenSizePerspectiveEnabledBooleanSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.4
Apply perspective scaling to screen-size point symbols in a SceneView. When
true, screen sized objects such as icons, labels or callouts integrate better in the 3D scene by applying a certain perspective projection to the sizing of features. This only applies when using a SceneView.layer.screenSizePerspectiveEnabled = true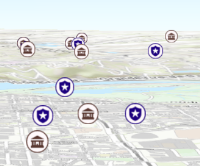
layer.screenSizePerspectiveEnabled = false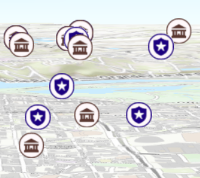
Known Limitations
Screen size perspective is currently not optimized for situations where the camera is very near the ground, or for scenes with point features located far from the ground surface. In these cases it may be better to turn off screen size perspective. As screen size perspective changes the size based on distance to the camera, it should be set to false when using size visual variables.
- Default Value:true
- spatialReferenceSpatialReferenceautocastSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
The spatial reference of the layer. The default value is WGS84. This property can be set explicitly to project the longitude and latitude coordinates when the layer parses the CSV file. While not required, explicitly setting the spatial reference of the layer will improve the performance when projecting to a spatial reference other than the one used by the coordinates in the raw data.
Known Limitations
The browser must support WebAssembly if a spatial reference other than WGS84 or Web Mercator is specified.
- Default Value:SpatialReference.WGS84
- See also:
Example:const csvLayer = new CSVLayer({ url: "example.csv", spatialReference: { wkid: 5936 } });
- titleString
The title of the layer used to identify it in places such as the Legend and LayerList widgets.
When the layer is loaded from a portal item, the title of the portal item will be used. If a layer is loaded as part of a webmap or a webscene, then the title of the layer as stored in the webmap/webscene will be used.
- urlString
The URL of the CSV file.
Indicates if the layer is visible in the View. When
false, the layer may still be added to a Map instance that is referenced in a view, but its features will not be visible in the view.- Default Value:true
Example:// The layer is no longer visible in the view layer.visible = false;
Method Overview
| Name | Return Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cancels a load() operation if it is already in progress. more details | more details | Layer | ||
| Query | Creates query parameters that can be used to fetch features that satisfy the layer's current filters, and definitions. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
Emits an event on the instance. more details | more details | Layer | ||
| Boolean | Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Boolean |
| more details | Layer | |
| Boolean |
| more details | Layer | |
| Boolean |
| more details | Layer | |
| Promise | Loads the resources referenced by this class. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Object | Registers an event handler on the instance. more details | more details | Layer | |
| Promise<Object> | Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns the Extent of features that satisfy the query. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Promise<Number> | Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns the number of features that satisfy the query. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Promise<FeatureSet> | Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns a FeatureSet, which can be accessed using the | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Promise<Number[]> | Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns an array of Object IDs for features that satisfy the input query. more details | more details | CSVLayer | |
| Promise |
| more details | Layer |
Method Details
- createQuery(){Query}Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Creates query parameters that can be used to fetch features that satisfy the layer's current filters, and definitions.
Returns:Type Description Query The query object representing the layer's filters and other definitions. Example:// Get a query object for the layer's current configuration const queryParams = layer.createQuery(); // set a geometry for querying features by the view's extent queryParams.geometry = view.extent; // Add to the layer's current definitionExpression queryParams.where = queryParams.where + " AND TYPE = 'Extreme'"; // query the layer with the modified params object layer.queryFeatures(queryParams) .then(function(results){ // prints the array of result graphics to the console console.log(results.features); });
- emit(type, event)inheritedSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.5
Emits an event on the instance. This method should only be used when creating subclasses of this class.
Parameters:type StringThe name of the event.
event ObjectThe event payload.
Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name.
Parameter:type StringThe name of the event.
Returns:Type Description Boolean Returns true if the class supports the input event.
isFulfilled()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is fulfilled (either resolved or rejected). If it is fulfilled,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been fulfilled (either resolved or rejected).
isRejected()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is rejected. If it is rejected,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been rejected.
isResolved()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is resolved. If it is resolved,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been resolved.
Loads the resources referenced by this class. This method automatically executes for a View and all of the resources it references in Map if the view is constructed with a map instance.
This method must be called by the developer when accessing a resource that will not be loaded in a View.
Returns:Type Description Promise Resolves when the resources have loaded.
Registers an event handler on the instance. Call this method to hook an event with a listener.
Parameters:type StringThe name of event to listen for.
listener FunctionThe function to call when the event is fired.
Returns:Type Description Object Returns an event handler with a remove()method that can be called to stop listening for the event.Property Type Description remove Function When called, removes the listener from the event. - See also:
Example:view.on("click", function(event){ // event is the event handle returned after the event fires. console.log(event.mapPoint); });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns the Extent of features that satisfy the query. If no parameters are specified, then the extent and count of all features satisfying the layer's configuration/filters are returned.
Known Limitations
- Spatial queries have the same limitations as those listed in the projection engine documentation.
- Spatial queries are currently not supported if the layer view has any of the following SpatialReferences:
- GDM 2000 (4742) – Malaysia
- Gusterberg (Ferro) (8042) – Austria/Czech Republic
- ISN2016 (8086) - Iceland
- SVY21 (4757) - Singapore
Parameter:optional Autocasts from ObjectSpecifies the attributes and spatial filter of the query. When no parameters are passed to this method, all features in the client are returned. To only return features visible in the view, set the
geometryparameter in the query object to the view's extent.Returns:Type Description Promise<Object> When resolved, returns the extent and count of the features that satisfy the input query. See the object specification table below for details. Property Type Description count Number The number of features that satisfy the input query. extent Extent The extent of the features that satisfy the query. Example:// Queries for the extent of all features // zooms to the extent csvLayer.when(function () { csvLayer.queryExtent().then(function (results) { view.goTo(results.extent); }) .catch(function (error) { console.log(error) }); });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns the number of features that satisfy the query. If no parameters are specified, then the total number of features satisfying the layer's configuration/filters is returned.
Known Limitations
- Spatial queries have the same limitations as those listed in the projection engine documentation.
- Spatial queries are currently not supported if the layer view has any of the following SpatialReferences:
- GDM 2000 (4742) – Malaysia
- Gusterberg (Ferro) (8042) – Austria/Czech Republic
- ISN2016 (8086) - Iceland
- SVY21 (4757) - Singapore
Parameter:optional Autocasts from ObjectSpecifies the attributes and spatial filter of the query. When no parameters are passed to this method, all features in the client are returned. To only return features visible in the view, set the
geometryparameter in the query object to the view's extent.Returns:Type Description Promise<Number> When resolved, returns an the number of features satisfying the query. Example:// returns all features in the CSVLayer csvLayer.queryFeatureCount().then(function (count) { console.log("Feature count: ", count); }) .catch(function (error) { console.log(error) });
- queryFeatures(params){Promise<FeatureSet>}Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns a FeatureSet, which can be accessed using the
.then()method once the promise resolves. A FeatureSet contains an array of Graphic features, which can be added to the view's graphics. This array will not be populated if zero results are found.Known Limitations
- Spatial queries have the same limitations as those listed in the projection engine documentation.
- Spatial queries are not currently supported if the layer view has any of the following SpatialReferences:
- GDM 2000 (4742) – Malaysia
- Gusterberg (Ferro) (8042) – Austria/Czech Republic
- ISN2016 (8086) - Iceland
- SVY21 (4757) - Singapore
Parameter:optional Autocasts from ObjectSpecifies the attributes and spatial filter of the query. When no parameters are passed to this method, all features in the client are returned. To only return features visible in the view, set the
geometryparameter in the query object to the view's extent.Returns:Type Description Promise<FeatureSet> When resolved, a FeatureSet containing an array of graphic features is returned. Examples:// Queries for all the features csvLayer.queryFeatures().then(function(results){ // prints the array of result graphics to the console console.log(results.features); });// Queries for all the features that matches the where clause var csvLayer = new CSVLayer({ url: "urlToService" }); csvLayer.load().then(function(){ var query = new Query({ where: "mag > 5", returnGeometry: true }); return csvLayer.queryFeatures(query); }) .then(function(results){ displayResults(results); }) .catch(function (error) { console.log(error) });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Executes a Query against the CSV data and returns an array of Object IDs for features that satisfy the input query. If no parameters are specified, then the Object IDs of all features satisfying the layer's configuration/filters are returned.
Known Limitations
- Spatial queries have the same limitations as those listed in the projection engine documentation.
- Spatial queries are currently not supported if the layer view has any of the following SpatialReferences:
- GDM 2000 (4742) – Malaysia
- Gusterberg (Ferro) (8042) – Austria/Czech Republic
- ISN2016 (8086) - Iceland
- SVY21 (4757) - Singapore
Parameter:optional Autocasts from ObjectSpecifies the attributes and spatial filter of the query. When no parameters are passed to this method, all features in the client are returned. To only return features visible in the view, set the
geometryparameter in the query object to the view's extent.Returns:Type Description Promise<Number[]> When resolved, returns an array of numbers representing the object IDs of the features satisfying the query. Examples:// Queries for all the Object IDs of features csvLayer.queryObjectIds().then(function(results){ // prints the array of Object IDs to the console console.log(results); });const query = new Query({ where: "state = California" }); //query objectIds of features belonging to California csvLayer.queryObjectIds(query).then(function(ids){ console.log(ids); // an array of object IDs });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.6
when()may be leveraged once an instance of the class is created. This method takes two input parameters: acallbackfunction and anerrbackfunction. Thecallbackexecutes when the instance of the class loads. Theerrbackexecutes if the instance of the class fails to load.Parameters:callback FunctionoptionalThe function to call when the promise resolves.
errback FunctionoptionalThe function to execute when the promise fails.
Returns:Type Description Promise Returns a new promise for the result of callbackthat may be used to chain additional functions.Example:// Although this example uses MapView, any class instance that is a promise may use then() in the same way var view = new MapView(); view.when(function(){ // This function will execute once the promise is resolved }, function(error){ // This function will execute if the promise is rejected due to an error });
Event Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
{view: View,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after the layer's LayerView is created and rendered in a view. more details | more details | Layer | |
{view: View,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after the layer's LayerView is destroyed and no longer renders in a view. more details | more details | Layer |
Event Details
- layerview-createinherited
Fires after the layer's LayerView is created and rendered in a view.
- Properties:
- view View
The view in which the
layerViewwas created.layerView LayerViewThe LayerView rendered in the view representing the layer in
layer. - See also:
Example:// This function will fire each time a layer view is created for this // particular view. layer.on("layerview-create", function(event){ // The LayerView for the layer that emitted this event event.layerView; });