SceneView
require(["esri/views/SceneView"], function(SceneView) { /* code goes here */ });esri/views/SceneView- Overview
- Using the view
- SceneView navigation
- SceneView navigation with gamepad and 3DConnexion devices
- Programmatic navigation
- Viewing modes
- Supported Coordinate Systems
- Using elevation data
Overview
A SceneView displays a 3D view of a Map or WebScene instance using WebGL. To render a map and its layers in 2D, see the documentation for MapView. For a general overview of views, see View.
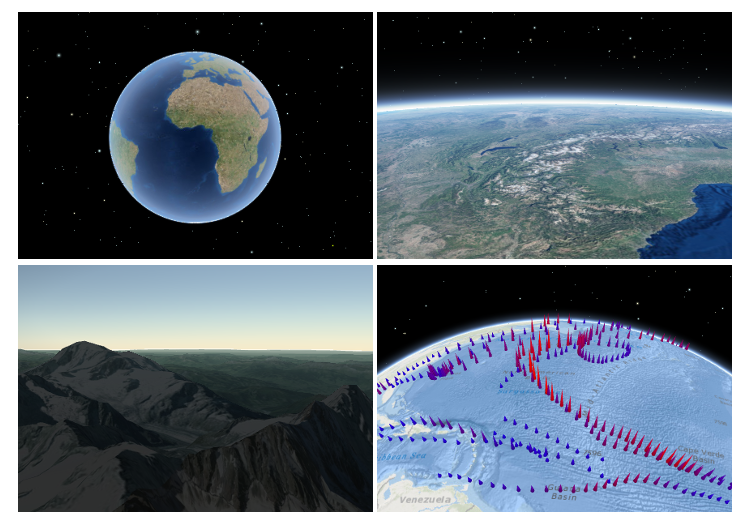
For a map to be visible to the user in the DOM, a SceneView must have both a valid Map instance and a DOM element with a non-zero height and width in which to render. Note that there must be valid data in the map, such as operational layers or a basemap with base layers, before the view will begin rendering the map.
// Create a basic SceneView instance with a basemap and world elevation
const view = new SceneView({
// An instance of Map or WebScene
map: new Map({
basemap: "hybrid"
}),
// The id of a DOM element (may also be an actual DOM element)
container: "viewDiv"
});
Known Limitations
The number of features that can be rendered in a SceneView varies depending on the complexity of each feature's geometry and symbol.
Point layers with a large number of features can be loaded and visualized in a SceneView. The features are dynamically loaded and displayed as you navigate the scene. For optimal performance, the number of displayed features is adjusted based on the complexity of the symbol and device capability. As a result, some features may not be visible in the view.
For lines and polygons all the features are displayed in the view, independent of the point symbol or the device. For best performance, we recommend to limit the number of features to 2,000.
Read more
Using the view
A SceneView may not be immediately ready for display after it has been constructed. For example, map data may need to be loaded first to determine the spatialReference of the view, or the DOM container may not yet have a non-zero size. Many of the view methods (such as hitTest or goTo) need the view to be ready before they can be used.
// create a SceneView instance (for 3D viewing)
const view = new SceneView({
map: new Map({
basemap: "topo"
}),
container: "viewDiv"
});
view.when(function() {
// SceneView is now ready for display and can be used. Here we will
// use goTo to view a particular location at a given zoom level, camera
// heading and tilt.
view.goTo({
center: [-112, 38],
zoom: 13,
heading: 30,
tilt: 60
})
})
.catch(function(err) {
// A rejected view indicates a fatal error making it unable to display,
// this usually means that WebGL is not available, or too old.
console.error("SceneView rejected:", err);
});
For live examples of view.when(), see the 2D overview map in SceneView and Toggle elevation layer samples.
SceneView navigation
The view can be navigated programmatically via goTo() and the view properties or interactively with mouse, keyboard or touch inputs. SceneView navigation is enabled by defaults, and includes the mouse, keyboard and touch interactions as described in the table below. Touch interactions are working on any touch enabled monitor or laptop screen.
| Action | SceneView behavior |
|---|---|
| Drag | Pan |
| Double-click | Zoom in at the cursor |
| Scroll forward | Zoom in at the cursor |
| Scroll backward | Zoom out at the center of the view |
| Right-click+Drag | 3D-rotate around the center of the view |
| Arrow Keys | Nudge the view left, right, up, or down (only supported in global scene) |
| B + Left-click+Drag | 3D-rotate around the camera's position |
| P | Move the camera to look perpendicular to the data displayed in the view |
| N | Adjust the SceneView to point north |
| J | Move down, closer to the view (only supported in global scene) |
| U | Move up, higher from the view (only supported in global scene) |
| Drag with one or multiple fingers | Pan |
| Double-tap with one finger | Zoom in at the finger position |
| Two finger pinch in/out | Zoom out/in |
| Move two fingers in clockwise or counterclockwise direction | Rotate |
| Drag two fingers up or down the screen | Tilt the scene |
To disable SceneView navigation, you must call the stopPropagation() method on the event objects of the pointer or gesture events that trigger the navigation.
See our samples on disabling view navigation for examples.
SceneView navigation with Gamepad and 3DConnexion devices
Gamepad and 3Dconnexion devices, like the SpaceMouse, can be used for navigation when view.navigation.gamepad.enabled is set to true(default). Please see GamepadInputDevice for supported devices.
| Gamepad Action | SceneView behavior |
|---|---|
| Left Trigger | Descend |
| Right Trigger | Ascend |
| Left Stick | Pan |
| Right Stick | 3D-rotate around the center of the view |
| Action Image | SpaceMouse Action | SceneView behavior |
|---|---|---|
 | Push (left/right/forward/backward) | Pan |
 | Pull up | Ascend |
 | Push down | Descend |
 | Rotate clockwise | Rotate the view clockwise |
 | Rotate counterclockwise | Rotate the view counterclockwise |
 | Tilt | Tilt the scene |
To disable gamepad navigation, you can set view.navigation.gamepad.enabled to false.
Programmatic navigation
Traditional 2D mapping properties, such as scale, zoom, center and extent do not always work well in 3D. For example, a map's scale is not clear when viewed in the context of a globe. The SceneView therefore supports these properties on a best effort basis, with certain limitations (see the documentation of individual properties for more information).
// Compatibility with 2D viewing properties, such as center and zoom, allows
// convenient transitioning from the familiar use of the 2D MapView to the
// use of the SceneView for 3D viewing.
const view = new SceneView({
map: new Map({
basemap: "satellite"
}),
container: "viewDiv",
// Sets the center point of the view at a specified lon/lat
center: [-112, 38],
// Sets the zoom LOD to 13
zoom: 13
});
The nature of 3D viewing includes oblique views, z-values, and rotation, all of which add complexity to defining what is visible in the view. In contrast to 2D MapView, which are primarily defined by an extent, or center and scale, the primary view specification of the SceneView is a Camera instance. The camera is defined by a 3D position, heading and tilt. See the documentation of Camera for more details.
Because some view properties overlap (e.g. center and camera), there is a set priority in which these properties are applied during construction of the view (until the view becomes ready). The following table describes which properties have priority during view construction (properties that are overridden will have no effect during construction).
| Property | Overrides |
|---|---|
| camera | viewpoint, extent, center, scale, zoom |
| viewpoint | extent, center, scale, zoom |
| extent | center, scale, zoom |
| scale | zoom |
It can be difficult to define the camera for viewing data at a particular location. The goTo method provides a convenient way to set the view's camera based on data (geometries, graphics) you want to view and from any perspective using heading, tilt, scale or zoom. Additionally, goTo will provide a smooth transition to the new location of the view by default.
// go to a location specified in geographic coordinates,
// from a 45 degree angle.
view.goTo({
center: [-112, 38],
heading: 45
});
// go to view all the graphics in view.graphics, while northing the
// the camera and tilting it to 60 degrees
view.goTo({
target: view.graphics,
heading: 0,
tilt: 60
});
// Set the view to show an extent at a -20 degree heading, disabling the
// animated transition
view.goTo({
target: new Extent(694942, 5596444, 1284090, 6163926, SpatialReference.WebMercator),
heading: -20
}, {
animate: false
});
Viewing modes
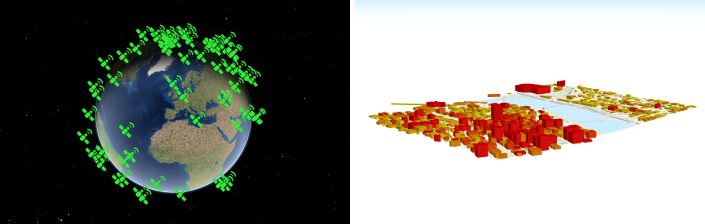
The SceneView supports two different viewing modes, global (left picture above) and local (right picture above), specified by the viewingMode property. Global scenes render the earth as a globe, while local scenes render the surface on a flat plane. Local mode allows for navigation and feature display in a localized or clipped area. In both viewing modes the users may navigate the camera below the ground surface by setting the esri/Ground#navigationConstraint#type to none.
The viewing mode (if not explicitly set by the user) is determined based on the spatial reference of the view. If the spatial reference is either Web Mercator or WGS84, then the viewingMode will default to global. For any other spatial reference the viewingMode will default to local.
Supported coordinate systems
The SceneView supports following coordinate systems in a global scene:
- WGS84 or WebMercator
- Noncached layers with any spatial reference since they will be reprojected to the scene spatial reference
In a local scene the following coordinate systems are supported:
- Any Projected Coordinate System
- Noncached layers with any spatial reference since they will be reprojected to the scene spatial reference
Using elevation data
The SceneView will use elevation layers from the Map.ground as sources for elevation when rendering the ground surface. Similar to the basemap, the ground can be initialized with a well-known name, which creates it with a known set of elevation layers.
const view = new SceneView({
map: new Map({
basemap: "satellite",
// A ground preset containing a single elevation layer, sourced from
// https://elevation3d.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/WorldElevation3D/Terrain3D/ImageServer
ground: "world-elevation"
},
container: "viewDiv"
});
Local elevation layers can be added to the ground.layers to merge multiple elevation sources into a single surface. See 3D Map With Elevation Services for an example.
- See also:
Constructors
- new SceneView(properties)
- Parameter:properties Objectoptional
See the properties for a list of all the properties that may be passed into the constructor.
Example:// Typical usage const view = new SceneView({ // ID of DOM element containing the view container: "viewDiv", // Map/WebScene object map: new Map() });
Property Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection<LayerView> | Collection containing a flat list of all the created LayerViews related to the basemap, operational layers, and group layers in this view. more details | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Allows the view to be partially or fully transparent when composited with the webpage elements behind it. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| ViewAnimation | Represents an ongoing view animation initialized by goTo(). more details | more details | View | |
| Object | A convenience property used for defining the breakpoints on the height and width of the view. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Camera | The observation point from which the visible portion (or perspective) of the SceneView is determined. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Point | Represents the view's center point; when setting the center you may pass a Point instance or an array of numbers representing at longitude/latitude pair ( | more details | SceneView | |
| Extent | Represents an optional clipping area used to define the visible extent of a local scene. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Accessor | Specifies constraints for Camera tilt and altitude that may be applied to the SceneView. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| HTMLDivElement | The | more details | View | |
| String | The name of the class. more details | more details | Accessor | |
| Accessor | Specifies various properties of the environment's visualization in the view. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Extent | The extent represents the visible portion of a map within the view as an instance of Extent. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Boolean | Indicates if the browser focus is on the view. more details | more details | View | |
| Collection<Graphic> | Allows for adding graphics directly to the default graphics in the View. more details | more details | View | |
| GroundView | The view for the ground of the map. more details | more details | View | |
| Number | The height of the view in pixels read from the view container element. more details | more details | View | |
| String | A convenience property indicating the general size of the view's height. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Object | Options for configuring the highlight. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Input | Options to configure input handling of the View. more details | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Indication whether the view is being interacted with (for example when panning). more details | more details | View | |
| Collection<LayerView> | A collection containing a hierarchical list of all the created LayerViews of the operational layers in the map. more details | more details | View | |
| Map | An instance of a Map object to display in the view. more details | more details | View | |
| Navigation | Options to configure the navigation behavior of the View. more details | more details | View | |
| String | A convenience property indicating the view's orientation. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Object | Use the padding property to make the center, and extent, etc. more details | more details | View | |
| Popup | A Popup object that displays general content or attributes from layers in the map. more details | more details | View | |
| String | SceneView can draw scenes in three different quality modes: | more details | SceneView | |
| Boolean | When | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Indicates if the view is being resized. more details | more details | View | |
| Number | Represents the current value of one pixel in the unit of the view's spatialReference. more details | more details | View | |
| Number | Represents an approximation of the map scale at the center of the view. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Number[] | An array containing the width and height of the view in pixels, e.g. more details | more details | View | |
| SpatialReference | The spatial reference of the view. more details | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Indication whether the view is animating, being interacted with or resizing. more details | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Indicates if the view is visible on the page. more details | more details | View | |
| String | The type of the view is either | more details | View | |
| DefaultUI | Exposes the default widgets available in the view and allows you to toggle them on and off. more details | more details | View | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether the view is being updated by additional data requests to the network, or by processing received data. more details | more details | View | |
| String | The viewing mode ( | more details | SceneView | |
| Viewpoint | Represents the current view as a Viewpoint or point of observation on the view. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Number | The width of the view in pixels read from the view container element. more details | more details | View | |
| String | A convenience property indicating the general size of the view's width. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Number | Represents the level of detail (LOD) at the center of the view. more details | more details | SceneView |
Property Details
- allLayerViewsCollection<LayerView> inherited
Collection containing a flat list of all the created LayerViews related to the basemap, operational layers, and group layers in this view.
- See also:
- alphaCompositingEnabledBooleanSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.8
Allows the view to be partially or fully transparent when composited with the webpage elements behind it. This property can only be set once at construction time. When alpha compositing is enabled, web scenes are less performant. It's important to set this property to
trueonly when you need to apply transparency on the view.- Default Value:false
Example:// create a view with a fully transparent background const view = new SceneView({ map: map, alphaCompositingEnabled: true, environment: { background: { type: "color", color: [0, 0, 0, 0] }, starsEnabled: false, atmosphereEnabled: false } })
- animationViewAnimation inherited
Represents an ongoing view animation initialized by goTo(). You may watch this property to be notified when the view's extent changes .
- See also:
- breakpointsObject
A convenience property used for defining the breakpoints on the height and width of the view. The sizes specified here determine the values of the widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint properties depending on the view's size.
Setting up breakpoints can aid in responsive app design. It does this by watching width and height breakpoints. This is helpful as it removes the need for multiple
@mediacalls. Instead of listening for the view's size and/or resizes property, you can set up a watch handler for either the widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint properties of the view.Please refer to the styling guide for additional information on working with this.
- Properties:
- optionalxsmall NumberDefault Value:544
Sets the
xsmallbreakpoint in pixels used by widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint. If the view's height or width is smaller than this value, then the value of widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint will bexsmall.optionalsmall NumberDefault Value:768Sets the
smallbreakpoint in pixels used by widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint. If the view's height or width is between this value and the value of thexsmallproperty, then the value of widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint will besmall.optionalmedium NumberDefault Value:992Sets the
mediumbreakpoint in pixels used by widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint. If the view's height or width is between this value and the value of thesmallproperty, then the value of widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint will bemedium.optionallarge NumberDefault Value:1200Sets the
largebreakpoint in pixels used by widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint. If the view's height or width is between this value and the value of themediumproperty, then the value of widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint will belarge.optionalxlarge NumberSets the
xlargebreakpoint in pixels used by widthBreakpoint and heightBreakpoint. If the view's height or width is greater than the value of thelargeproperty, then the value of widthBreakpoint or heightBreakpoint will bexlarge. - See also:
Example:// Instead of watching the size or resizing properties view.watch(size) view.watch(resizing) // Set up a watch handle for breakpoint view.watch("widthBreakpoint",function(breakpoint){ switch (breakpoint) { case "xsmall": // do something break; case "small": case "medium": case "large": case "xlarge": // do something else break; default: } });
The observation point from which the visible portion (or perspective) of the SceneView is determined. Contains properties including the elevation, tilt, and heading (in degrees) of the current view. Setting the camera immediately changes the current view. For animating the view, see goTo().
When set in the constructor, this property overrides the viewpoint, extent, center, scale, and zoom properties.
The camera property contains an internal reference which may be modified in the future. To persist or modify the camera, create a clone using camera.clone().
Z-values defined in a geographic or metric coordinate system are expressed in meters. However, in local scenes that use a projected coordinate system, vertical units are assumed to be the same as the horizontal units specified by the service.
- See also:
Examples:// Initializes the view at the given (x, y, z) position with a heading of 95 degrees. // The position of the camera is a Point which will autocast in the sample // below. Note that the default Point spatial reference is WGS84 which // will only work if the SceneView has a Web Mercator or WGS84 spatial // reference. For other spatial references, create a new position Point // with an explicit spatial reference. const view = new SceneView({ camera: { position: [ -122, // lon 38, // lat 50000 // elevation in meters ], heading: 95 } });// Initializes the view at the given position with a tilt of 65 degrees const view = new SceneView({ camera: { position: { x: -100, // lon y: 45, // lat z: 10654 // elevation in meters }, tilt: 65 } });// Clone the camera to modify its properties const camera = view.camera.clone(); // Set new values for heading and tilt camera.heading = 180; camera.tilt = 45; // Set the new properties on the view's camera view.camera = camera;// Set the view's camera to a new position, heading and tilt with the goTo() method view.goTo({ target: [-122, 38, 50000], heading: 180, tilt: 45 });
Represents the view's center point; when setting the center you may pass a Point instance or an array of numbers representing at longitude/latitude pair (
[-100.4593, 36.9014]). Setting the center immediately changes the current view. For animating the view, see goTo().If set in the constructor, this property will be ignored if the viewpoint, camera, or extent properties are also set in the constructor.
The center property contains an internal reference which may be modified in the future. To persist or modify the center, create a clone using center.clone().
Z-values defined in a geographic or metric coordinate system are expressed in meters. However, in local scenes that use a projected coordinate system, vertical units are assumed to be the same as the horizontal units specified by the service.
- See also:
Examples:// Sets the initial center point of the view to long/lat coordinates const view = new SceneView({ center: [-112, 38] });// Updates the view's center point to a pre-determined Point object view.center = new Point({ x: 12804.24, y: -1894032.09, z: 12000, spatialReference: 2027 });// view.center needs to be set (not modified in place) to have an effect. // To modify only the center.x, first clone the current center, modify // the .x property and then set it on the view. const center = view.center.clone(); // Offset the center 1km to the east center.x += 1000; view.center = center;
Represents an optional clipping area used to define the visible extent of a local scene. If defined, only data (including the basemap) within the area will be displayed.
The
clippingAreaproperty only applies to local scenes.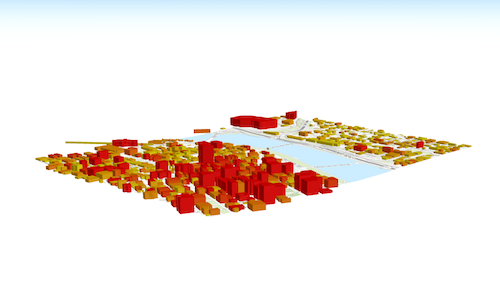
The clippingArea property contains an internal reference which may be modified in the future. To persist or modify the clippingArea, create a clone using clippingArea.clone().
Example:const extent = view.extent.clone(); // Expand the extent in place, reducing it to 50% of its original size // and set it as the clippingArea view.clippingArea = extent.expand(0.5);
Specifies constraints for Camera tilt and altitude that may be applied to the SceneView. See the object specification table below for details.
- Properties:
- optionalaltitude Accessor
Specifies a constraint on the minimum and maximum allowed camera altitude.
optionalclipDistance AccessorSpecifies the near and far webgl clip distances.
- Specification:
- optionalnear Number
The near clip distance.
optionalfar NumberThe far clip distance.
optionalmode StringDefault Value:autoSpecifies the mode of the constraint which is either
autoormanual. Inautomode, the near and far clip distance values are automatically determined. Inmanualmode, the near and far clip distance values are user defined, constant values. Note that the mode automatically changes tomanualwhenever thenearorfarproperty is set.
optionalcollision ObjectWhen enabled, prevents the user from navigating below the surface in a local SceneView. This property is deprecated, please use Ground instead.
Deprecated since version 4.8
- Specification:
- optionalenabled BooleanDefault Value:true
Set to
falseto permit the user to navigate below the surface in a local SceneView.
optionaltilt AccessorSpecifies a constraint on the amount of allowed tilting of the view.
- Specification:
- optionalmax Number
Specifies the maximum amount of tilt (in degrees) allowed in the view and may range from 0.5 to 179.5 degrees.
optionalmode StringDefault Value:autoSpecifies the mode of the constraint. There are two possible values:
autoormanual. Inautomode, the maximum tilt value is automatically determined based on the altitude of the view camera. Inmanualmode, the maximum tilt value is a user defined, constant value. Note: The mode automatically changes tomanualwhenever themaxproperty is set.
- See also:
- Autocasts from String
The
idor node representing the DOM element containing the view. This is typically set in the view's constructor.Examples:// Sets container to the DOM id var view = new MapView({ container: "viewDiv" // ID of the HTML element that holds the view });// Sets container to the node var viewNode = document.getElementById("viewDiv"); var view = new SceneView({ container: viewNode });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
The name of the class. The declared class name is formatted as
esri.folder.className.
- environmentAccessor
Specifies various properties of the environment's visualization in the view. The SceneView will redraw automatically when any property of environment changes.
const view = new SceneView({ map: map, container: "viewDiv" }); // Set the sun position to reflect the current time view.environment.lighting.date = Date.now(); // Disable automatic lighting updates by camera tracking view.environment.lighting.cameraTrackingEnabled = true; // Set a background color const view = new SceneView({ container: "view", map: map, environment: { background: { type: "color", color: [255, 252, 244, 1] }, starsEnabled: false, atmosphereEnabled: false } });- Properties:
- optionalbackground Background
Specifies how the background of the scene (which lies behind sky, stars and atmosphere) should be displayed. By default this is simply a single, fully opaque, black color. Currently ColorBackground is the only type of background supported.
optionallighting AccessorLighting conditions of the scene.
- Specification:
- optionaldate DateDefault Value:new Date("March 15, 2015 12:00:00")
The current date and time of the simulated sun.
optionaldirectShadowsEnabled BooleanDefault Value:falseIndicates whether to show shadows cast by the sun. Shadows are only displayed for real world 3D objects. Terrain doesn't cast shadows. In local scenes at small zoom levels, shadows are not displayed.
optionalambientOcclusionEnabled BooleanDefault Value:falseIndicates whether to show ambient occlusion shading.
optionalcameraTrackingEnabled BooleanDefault Value:trueIndicates whether the date and time of the simulated sun is automatically updated to maintain the current time of day while the camera changes.
optionalatmosphereEnabled BooleanIndicates whether atmosphere visualization is enabled.
optionalatmosphere AccessorAtmosphere conditions of the scene.
- Specification:
- optionalquality StringDefault Value:low
Indicates the quality of the atmosphere visualization. The quality of the atmosphere may have a significant impact on performance. This setting does not have any effect in local scenes.
Known Value Example low 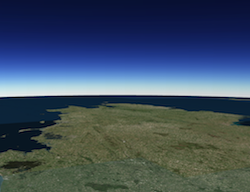
high 
optionalstarsEnabled BooleanDefault Value:trueIndicates whether stars visualization is enabled.
The extent represents the visible portion of a map within the view as an instance of Extent. Setting the extent immediately changes the view without animation. To animate the view, see goTo().
Rather than using extent to change the visible portion of the map in a SceneView, you should use camera since it easily allows you to define the heading, elevation and tilt of the observation point from which the view's perspective is created.
When set in the constructor, this property overrides the center, scale, and zoom properties. This property will be ignored if the viewpoint or camera are also set in the constructor.
The extent property contains an internal reference which may be modified in the future. To persist or modify the extent, create a clone using extent.clone().
Z-values defined in a geographic or metric coordinate system are expressed in meters. However, in local scenes that use a projected coordinate system, vertical units are assumed to be the same as the horizontal units specified by the service.
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Indicates if the browser focus is on the view.
- graphicsCollection<Graphic> inherited
Allows for adding graphics directly to the default graphics in the View.
Examples:// Adds a graphic to the View view.graphics.add(pointGraphic);// Removes a graphic from the View view.graphics.remove(pointGraphic);
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
The view for the ground of the map.
The height of the view in pixels read from the view container element.
The view container needs to have a height greater than 0 to be displayed.
- Default Value:0
- heightBreakpointString
A convenience property indicating the general size of the view's height. This value is determined based on where the view's height falls in the ranges defined in the breakpoints property. See the table below for a list of possible values. Use the breakpoints property to override the default thresholds.
Please refer to the styling guide for additional information on working with this.
Possible Value Description Default thresholds (pixels) xsmall The height of the view is smaller than the value set in the xsmallbreakpoint.< 545 small The height of the view is between the values set in the xsmallandsmallbreakpoints.545 - 768 medium The height of the view is between the values set in the smallandmediumbreakpoints.769 - 992 large The height of the view is between the values set in the mediumandlargebreakpoints.993 - 1200 xlarge The height of the view is larger than the value set in the largebreakpoint.> 1200 Example:view.watch("heightBreakpoint", function(newVal){ if (newVal === "xsmall"){ // clear the view's default UI components if // app is used on a mobile device view.ui.components = []; } });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.4
Options for configuring the highlight. Use the highlight method on the appropriate LayerView to highlight a feature.
- Properties:
- optionalcolor ColorDefault Value:#00ffff
The color of the highlight.
optionalhaloOpacity NumberDefault Value:1The opacity of the highlight halo. This will be multiplied with the opacity specified in
color.optionalfillOpacity NumberDefault Value:0.25The opacity of the fill (area within the halo). This will be multiplied with the opacity specified in
color. - See also:
Example:const view = new SceneView({ map: map, highlightOptions: { color: [255, 255, 0, 1], haloOpacity: 0.9, fillOpacity: 0.2 } });
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.9
Options to configure input handling of the View.
Example:// Make gamepad events to emit independently of focus. view.input.gamepad.enabledFocusMode = "none";
Indication whether the view is being interacted with (for example when panning).
- Default Value:false
- layerViewsCollection<LayerView> inherited
A collection containing a hierarchical list of all the created LayerViews of the operational layers in the map.
- See also:
An instance of a Map object to display in the view. A view may only display one map at a time. On the other hand, one Map may be viewed by multiple MapViews and/or SceneViews simultaneously.
This property is typically set in the constructor of the MapView or SceneView. See the class description for examples demonstrating the relationship between the map and the view.
- orientationStringreadonly
A convenience property indicating the view's orientation. See the table below for a list of possible values.
Please refer to the styling guide for additional information on working with this.
Possible Value Description landscape The width of the view is greater than its height. portrait The width of the view is equal to or smaller than its height.
Use the padding property to make the center, and extent, etc. work off a subsection of the full view. This is particularly useful when layering UI elements or semi-transparent content on top of portions of the view. See the view padding sample for an example of how this works.
A Popup object that displays general content or attributes from layers in the map.
The view has a default instance of Popup with predefined styles and a template for defining content. The content in this default instance may be modified directly in the popup's content or in a layer's PopupTemplate.
You may create a new Popup instance and set it to this property to customize the style, positioning, and content of the popup in favor of using the default popup instance on the view.
In addition, if wanting to prevent any popups from opening, use the syntax below:
Example:view.popup = null;
- qualityProfileString
SceneView can draw scenes in three different quality modes:
high,mediumandlow.The
lowquality profile significantly increases performance on slower browsers and devices by reducing the memory limit and the visual quality in the following aspects:- Map resolution
- Scene layer detail level
- Anti-aliasing (edge smoothing)
The high and medium quality profiles only differ in the maximum amount of memory which the view is allowed to use. A higher memory limit improves quality in complex web scenes with many layers, but can have a negative impact on drawing performance and stability.
The default value is based on the detected browser:
lowfor Internet Explorer 11 and certain mobile devicesmediumfor any other browser
Overriding the default value is best done in the constructor (see example below). If the value is modified after construction, only a subset of the quality aspects are affected.
Example:const view = new SceneView({ qualityProfile: "high" });
When
true, this property indicates whether the view successfully satisfied all dependencies, signaling that the following conditions are met.- The view has a map. If map is a WebMap or a WebScene, then the map or scene must be loaded.
- The view has a container with a size greater than
0. - The view has a spatialReference.
When a view becomes ready it will resolve itself and invoke the callback defined in when() where code can execute on a working view. Subsequent changes to a view's readiness would typically be handled by watching
view.readyand providing logic for cases where the map or container change.- Default Value:false
- See also:
Indicates if the view is being resized.
- Default Value:false
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.9
Represents the current value of one pixel in the unit of the view's spatialReference. The value of resolution is calculated by dividing the view's extent width by its width.
- scaleNumber
Represents an approximation of the map scale at the center of the view. Setting the scale immediately changes the current view. For animating the view, see goTo().
When set in the constructor, this property overrides the zoom property. This property will be ignored if the viewpoint, camera, or extent properties are also set in the constructor.
- See also:
Example:// Set the approximate map scale at the center the view to 1:24,000 view.scale = 24000;
An array containing the width and height of the view in pixels, e.g.
[width, height].
The spatial reference of the view. This indicates the Projected Coordinate System or the Geographic Coordinate System used to locate geographic features in the map. In a SceneView the following supported coordinate systems are available.
The spatial reference can either be set explicitly or automatically derived from the following:
- In the case of a SceneView, if the map is a WebScene instance, the WebScene.initialViewProperties.spatialReference is used.
- In all other cases, the spatial reference is derived from the first layer that loads in this order:
When using an Esri basemap, the default spatial reference is Web Mercator Auxiliary Sphere.
- Default Value:null
Indication whether the view is animating, being interacted with or resizing.
- Default Value:true
Indicates if the view is visible on the page. Is
trueif the view has no container, a height or width equal to 0, or the CSSvisibilityishidden.- Default Value:true
Exposes the default widgets available in the view and allows you to toggle them on and off. See DefaultUI for more details.
Examples:var toggle = new BasemapToggle({ view: view, nextBasemap: "hybrid" }); // Adds an instance of BasemapToggle widget to the // top right of the view. view.ui.add(toggle, "top-right");// Moves the zoom and BasemapToggle widgets to the // bottom left of the view. view.ui.move([ "zoom", toggle ], "bottom-left");// Removes all the widgets from the bottom left of the view view.ui.empty("bottom-left");// Removes the compass widget from the view view.ui.remove("compass");
Indicates whether the view is being updated by additional data requests to the network, or by processing received data.
- Default Value:false
- viewingModeString
The viewing mode (
localorglobal). Global scenes render the earth as a sphere. Local scenes render the earth on a flat plane and allow for navigation and feature display in a localized or clipped area. Users may also navigate the camera of a local scene below the surface of a basemap.Value Example Description global 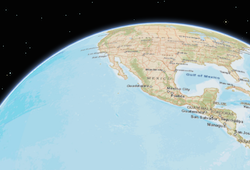
Global scenes allow the entire globe to render in the view, showing the curvature of the earth. local 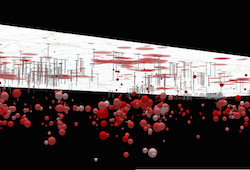
Local scenes render the earth on a flat surface. They can be constrained to only show a "local" area by setting the clippingArea property. Local scenes also allow for displaying and exploring data that would otherwise be hidden by the surface of the earth. Depending on the viewing mode different supported coordinate systems are available.
- Default Value:global
- See also:
Represents the current view as a Viewpoint or point of observation on the view. In SceneViews, camera should be used in favor of viewpoint for watching or changing the point of view. Setting the viewpoint immediately changes the current view. For animating the view, see goTo().
When set in the constructor, this property overrides the extent, center, scale, and zoom properties. This property will be ignored if camera is also set in the constructor.
The viewpoint property contains an internal reference which may be modified in the future. To persist or modify the viewpoint, create a clone using viewpoint.clone().
- See also:
The width of the view in pixels read from the view container element.
The view container needs to have a width greater than 0 to be displayed.
- Default Value:0
- widthBreakpointString
A convenience property indicating the general size of the view's width. This value is determined based on where the view's width falls in the ranges defined in the breakpoints property. See the table below for a list of possible values. Use the breakpoints property to override the default thresholds.
Please refer to the styling guide for additional information on working with this.
Possible Value Description Default thresholds (pixels) xsmall The width of the view is smaller than the value set in the xsmallbreakpoint.< 545 small The width of the view is between the values set in the xsmallandsmallbreakpoints.545 - 768 medium The width of the view is between the values set in the smallandmediumbreakpoints.769 - 992 large The width of the view is between the values set in the mediumandlargebreakpoints.993 - 1200 xlarge The width of the view is larger than the value set in the largebreakpoint.> 1200 Example:view.watch("widthBreakpoint", function(newVal){ if (newVal === "xsmall"){ // clear the view's default UI components if // app is used on a mobile device view.ui.components = []; } });
- zoomNumber
Represents the level of detail (LOD) at the center of the view. Setting the zoom immediately changes the current view. For animating the view, see goTo().
Setting this property in conjunction with center is a convenient way to set the initial extent of the view.
If set in the constructor, this property will be ignored if the viewpoint, camera, extent, or scale properties are also set in the constructor.
- See also:
Examples:view.zoom = 3; // Sets the LOD to 3 (small map scale) view.zoom = 18; // Sets the LOD to 18 (large map scale)// Set the zoom level and center in the constructor const view = new SceneView({ zoom: 10, center: [-120, 34], map: map });
Method Overview
| Name | Return Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Sets the focus on the view. more details | more details | View | ||
| Promise | Sets the view to a given target. more details | more details | SceneView | |
Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name. more details | more details | SceneView | ||
| Promise<HitTestResult> | Returns the topmost feature from each layer that intersects the specified screen coordinates. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Boolean |
| more details | View | |
| Boolean |
| more details | View | |
| Boolean |
| more details | View | |
| Object | Registers an event handler on the instance. more details | more details | View | |
| Promise<Screenshot> | Create a screenshot of the current view. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Point | Converts the given screen point to a map point. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| ScreenPoint | Converts the given map point to a screen point. more details | more details | SceneView | |
| Promise |
| more details | View | |
| Promise<LayerView> | Gets the LayerView created on the view for the given layer. more details | more details | View |
Method Details
- focus()inheritedSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.5
Sets the focus on the view.
- goTo(target, options){Promise}
Sets the view to a given target. The target parameter can be one of the following:
[longitude, latitude]pair of coordinates- Geometry (or array of Geometry[])
- Graphic (or array of Graphic[])
- Viewpoint
- Camera
- Object with a combination of
target,center,scale,position,headingandtiltproperties (withtargetbeing any of the types listed above). Thecenterproperty is provided as a convenience to animate the SceneView.center and is the equivalent of specifying thetargetwith the center Point. The target must be provided in the spatial reference of the view.
This function returns a promise which resolves as soon as the new view has been set to the target. If the transition is animated, then the ongoing animation can be obtained using SceneView.animation.
If the given target is far away from the current camera position, then heading and tilt will be automatically set to their neutral values (facing north, looking top down). Tilt and heading can always be explicitly set to override this behavior.
Parameters:The target location/viewpoint to go to. When using an object for
target, use the properties in the table below.Specification:optional The target of the animation.
optional The SceneView.center to go to.
scale NumberoptionalThe SceneView.scale to go to.
zoom NumberoptionalThe final zoom value to go to.
heading NumberoptionalThe Camera.heading to go to.
tilt NumberoptionalThe Camera.tilt to go to.
position PointoptionalThe Camera.position to go to.
options ObjectoptionalView transition options.
Specification:animate BooleanoptionalDefault Value: trueIndicates if the transition to the new view should be animated. If set to false,
speedFactor,duration,maxDuration, andeasingproperties are ignored.speedFactor NumberoptionalDefault Value: 1Increases or decreases the animation speed by the specified factor. A speedFactor of 2 will make the animation twice as fast, while a speedFactor of 0.5 will make the animation half as fast. Setting the speed factor will automatically adapt the default maxDuration accordingly.
duration NumberoptionalSet the exact duration (in milliseconds) of the animation. Note that by default, animation duration is calculated based on the time required to reach the target at a constant speed. Setting duration overrides the speedFactor option. Note that the resulting duration is still limited to the maxDuration.
maxDuration NumberoptionalDefault Value: 8000The maximum allowed duration (in milliseconds) of the animation. The default maxDuration value takes the specified speedFactor into account.
easing String|EasingFunctionoptionalThe easing function to use for the animation. This may either be a preset (named) function, or a user specified function. Supported named presets are:
linear,in-cubic,out-cubic,in-out-cubic,in-expo,out-expo,in-out-expo,in-out-coast-quadratic. See easing functions for graphical representations of these functions.By default, animations that are less than 1000 ms use the
out-expoeasing function; longer animations use thein-out-coast-quadraticeasing function.Returns:Type Description Promise A promise that resolves when the view is set to the target. - See also:
Examples:view.goTo({ center: [-126, 49], heading: 180, // set the heading to point South tilt: view.camera.tilt, // maintain tilt value })// go to a location defined by a Camera object const cam = new Camera({ position: new Point({ x: -100.23, // lon y: 65, // lat z: 10000, // elevation in meters }), heading: 180, // facing due south tilt: 45 // bird's eye view }); view.goTo(cam);// go to a point using center, zoom, tilt, and heading view.goTo({ center: [-126, 49], zoom: 13, tilt: 75, heading: 105 });// goTo returns a Promise which resolves when the animation has finished. // This promise may be chained to create a sequence of animations. view.goTo(graphic1) .then(function() { return view.goTo(graphic2); }) .then(function() { return view.goTo(graphic3); });// goTo returns a Promise which resolves when the animation has finished. // This promise may be chained to create a sequence of animations. view.goTo(graphic1) .then(function() { return view.goTo(graphic2); }) .then(function() { return view.goTo(graphic3); });
- hasEventListener()
Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name.
- hitTest(screenPoint){Promise<HitTestResult>}
Returns the topmost feature from each layer that intersects the specified screen coordinates. The following layer types will return a result if a hit is made on an intersecting feature: GraphicsLayer, FeatureLayer, CSVLayer, GeoRSSLayer, KMLLayer, and StreamLayer.
Draped graphics (i.e. graphics in layers where the elevation mode is
on-the-ground) are currently not returned from this method, even when they intersect the input screen point.When the ground surface is hit, but no graphic is found, then the result of hitTest will be a single object with its mapPoint set to the point on the surface that was hit, but its graphic will be set to
null.Parameters:screenPoint ObjectThe screen coordinates of the click on the view.
Specification:x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the click on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the click on the view.
Returns:Type Description Promise<HitTestResult> When resolved, returns an object containing the graphics (if present) that intersect the given screen coordinates. Example:// Get the screen point from the view's click event view.on("click", function(event) { const screenPoint = { x: event.x, y: event.y }; // Search for graphics at the clicked location view.hitTest(screenPoint).then(function(response) { const result = response.results[0]; if (result) { const lon = result.mapPoint.longitude; const lat = result.mapPoint.latitude; console.log("Hit surface at (" + lon + ", " + lat + "), graphic:", result.graphic || "none"); } }); });
isFulfilled()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is fulfilled (either resolved or rejected). If it is fulfilled,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been fulfilled (either resolved or rejected).
isRejected()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is rejected. If it is rejected,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been rejected.
isResolved()may be used to verify if creating an instance of the class is resolved. If it is resolved,truewill be returned.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether creating an instance of the class has been resolved.
Registers an event handler on the instance. Call this method to hook an event with a listener. See the Events summary table for a list of listened events.
Parameters:The name of the event or events to listen for.
Additional modifier keys to filter events. Please see Key Values for possible values. All the standard key values are supported. Alternatively, if no modifiers are required, the function will call when the event fires.
The following events don't support modifier keys:
blur,focus,layerview-create,layerview-destroy,resize.handler FunctionoptionalThe function to call when the event is fired, if modifiers were specified.
Returns:Type Description Object Returns an event handler with a remove()method that can be called to stop listening for the event.Property Type Description remove Function When called, removes the listener from the event. - See also:
Example:view.on("click", function(event){ // event is the event handle returned after the event fires. console.log(event.mapPoint); }); // Fires `pointer-move` event when user clicks on "Shift" // key and moves the pointer on the view. view.on('pointer-move', ["Shift"], function(evt){ var point = view2d.toMap({x: evt.x, y: evt.y}); bufferPoint(point); });
- takeScreenshot(options){Promise<Screenshot>}Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.9
Create a screenshot of the current view. Screenshots include only elements that are rendered on the canvas (all geographical elements), but excludes overlayed DOM elements (UI, popups, measurement labels, etc.). By default, a screenshot of the whole view is created. Different options allow for creating different types of screenshots, including taking screenshots at different aspect ratios, different resolutions and creating thumbnails.
Screenshots are always taken inside the padded area of the view (see padding).
Parameters:options ObjectoptionalScreenshot options.
Parameters:format StringoptionalDefault Value: jpgThe format of the resulting encoded data url.
Possible values: jpg | png.
quality NumberoptionalDefault Value: 98The quality (0 to 100) of the encoded image when encoding as
jpg.width NumberoptionalThe width of the screenshot (defaults to the area width). The height will be derived automatically if left unspecified, according to the aspect ratio of the of the screenshot area.
height NumberoptionalThe height of the screenshot (defaults to the area height). The width will be derived automatically if left unspecified, according to the aspect ratio of the screenshot area.
area ObjectoptionalSpecifies whether to take a screenshot of a specific area of the view. The area coordinates are relative to the origin of the padded view (see padding) and will be clipped to the view size. Defaults to the whole view (padding excluded).
Specification:x NumberoptionalThe x coordinate of the area.
y NumberoptionalThe y coordinate of the area.
width NumberoptionalThe width of the area.
height NumberoptionalThe height of the area.
Returns:Type Description Promise<Screenshot> When resolved, returns an object containing an encoded dataUrl and raw image data. Examples:// Take a screenshot at the same resolution of the current view view.takeScreenshot().then(function(screenshot) { var imageElement = document.getElementById("screenshotImage"); imageElement.src = screenshot.dataUrl; });// Create a square thumbnail from the current view var options = { width: 200, height: 200 }; view.takeScreenshot(options).then(function(screenshot) { var imageElement = document.getElementById("screenshotImage"); imageElement.src = screenshot.dataUrl; });// Take a high resolution, square screenshot var options = { width: 2048, height: 2048 }; view.takeScreenshot(options).then(function(screenshot) { var imageElement = document.getElementById("screenshotImage"); imageElement.src = screenshot.dataUrl; });// Take a screenshot of a small area at the center of the view // Compute the size of the view excluding potential padding var padding = view.padding; var innerWidth = view.width - padding.left - padding.right; var innerHeight = view.height - padding.top - padding.bottom; // Desired size of the area var width = 200; var height = 200; var options = { area: { x: (innerWidth - width) / 2, y: (innerHeight - height) / 2, width: width, height: height } }; view.takeScreenshot(options).then(function(screenshot) { var imageElement = document.getElementById("screenshotImage"); imageElement.src = screenshot.dataUrl; });
- toMap(screenPoint, mapPoint){Point}
Converts the given screen point to a map point.
Parameters:screenPoint ObjectThe screen coordinates to convert.
Specification:x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate to convert.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate to convert.
mapPoint PointoptionalThe point object that will reference the result.
Returns:Type Description Point The map point corresponding to the given screen point.
- toScreen(point, screenPoint){ScreenPoint}
Converts the given map point to a screen point.
Parameters:point PointA point geometry.
screenPoint ScreenPointoptionalScreenPoint object that will reference the result.
Returns:Type Description ScreenPoint The screen point corresponding to the given map point.
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.6
when()may be leveraged once an instance of the class is created. This method takes two input parameters: acallbackfunction and anerrbackfunction. Thecallbackexecutes when the instance of the class loads. Theerrbackexecutes if the instance of the class fails to load.Parameters:callback FunctionoptionalThe function to call when the promise resolves.
errback FunctionoptionalThe function to execute when the promise fails.
Returns:Type Description Promise Returns a new promise for the result of callbackthat may be used to chain additional functions.Example:// Although this example uses MapView, any class instance that is a promise may use then() in the same way var view = new MapView(); view.when(function(){ // This function will execute once the promise is resolved }, function(error){ // This function will execute if the promise is rejected due to an error });
Gets the LayerView created on the view for the given layer. The returned promise resolves when the layer view for the given layer has been created, or rejects with an error (for example if the layer is not part of the view, or if the layer type is not supported in this view).
Parameter:layer LayerThe layer for which to obtain its LayerView.
Returns:Type Description Promise<LayerView> Resolves to an instance of LayerView for the specified layer. - See also:
Example:// Create a feature layer from a url pointing to a Feature Service var layer = new FeatureLayer(url); map.add(layer); view.whenLayerView(layer) .then(function(layerView) { // The layerview for the layer }) .catch(function(error) { // An error occurred during the layerview creation });
Type Definitions
- EasingFunction(t, duration){Number}
User provided easing function. The function receives a normalized time between 0 and 1 as input and should provide a transformed normalized time between 0 and 1 as output.
Parameters:t NumberThe input time (from 0 to 1)
duration NumberThe total duration (in milliseconds) of the animation. This may be used for heuristics on deciding what type of easing to perform.
Returns:Type Description Number a value between 0 and 1 Example:// Simple quadratic ease in function function easeIn(t) { return t * t; }
- HitTestResult
Object specification for the result of the hitTest() method.
- Properties:
- results Object[]
An array of result objects returned from the hitTest(). Results are returned when the location of the input screen coordinates intersect a Graphic in the view. See the table below for the specification of each object in this array.
- Specification:
- graphic Graphic
A graphic present in the view that intersects the input screen coordinates. If the graphic comes from a layer with an applied Renderer, then the symbol property will be empty. Other properties will be empty based on the context in which the graphic is fetched.
mapPoint PointThe point geometry in the spatial reference of the view corresponding with the input screen coordinates.
- ScreenshotSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.9
Object returned when takeScreenshot() promise resolves:
Event Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
{target: View,native: Object} | Fires when browser focus is moved away from the view. more details | more details | View | |
{mapPoint: Point,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a user clicks on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{mapPoint: Point,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after double-clicking on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{action: String,x: Number,y: Number,origin: Object,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,radius: Number,angle: Number,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires during a pointer drag on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{target: View,native: Object} | Fires when browser focus is on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{mapPoint: Point,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after holding either a mouse button or a single finger on the view for a short amount of time. more details | more details | View | |
{mapPoint: Point,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires right after a user clicks on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{repeat: Boolean,key: String,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a keyboard key is pressed. more details | more details | View | |
{type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a keyboard key is released. more details | more details | View | |
{layer: Layer,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after each layer in the map has a corresponding LayerView created and rendered in the view. more details | more details | View | |
{layer: Layer,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after a LayerView is destroyed and is no longer rendered in the view. more details | more details | View | |
{x: Number,y: Number,deltaY: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires when a wheel button of a pointing device (typically a mouse) is scrolled on the view. more details | more details | View | |
{pointerId: Number,pointerType: String,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a mouse button is pressed, or a finger touches the display. more details | more details | View | |
{pointerId: Number,pointerType: String,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a mouse cursor enters the view, or a display touch begins. more details | more details | View | |
{pointerId: Number,pointerType: String,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a mouse cursor leaves the view, or a display touch ends. more details | more details | View | |
{pointerId: Number,pointerType: String,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after the mouse or a finger on the display moves. more details | more details | View | |
{pointerId: Number,pointerType: String,x: Number,y: Number,button: Number,buttons: Number,type: String,stopPropagation: Function,timestamp: Number,native: Object} | Fires after a mouse button is released, or a display touch ends. more details | more details | View | |
{oldWidth: Number,oldHeight: Number,width: Number,height: Number} | Fires when the view's size changes. more details | more details | View |
Event Details
- blurinheritedSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Fires when browser focus is moved away from the view.
- Properties:
- target View
The view that the browser focus is moved away from.
native ObjectA standard DOM KeyboardEvent.
- clickinherited
Fires after a user clicks on the view. This event emits slightly slower than a pointer-down event to make sure that a double-click event isn't triggered instead. The immediate-click event can be used for responding to a click event without delay.
- Properties:
- mapPoint Point
The point location of the click on the view in the spatial reference of the map.
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the click on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the click on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates the current mouse button state.
Value Description 0 left click (or touch) 1 middle click 2 right click type StringFor click the type is always
click.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
By default the
clickevent will close the view's popup if the clicked location doesn't intersect a feature containing a PopupTemplate. If calling view.popup.open() to display custom content in the popup, you should callevent.stopPropagation()on theclickevent object to disable this default behavior. This ensures the popup will remain open or open with new custom content when the user clicks other locations in the view.timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
- See also:
Examples:// Set up a click event handler and retrieve the screen point view.on("click", function(event) { // the hitTest() checks to see if any graphics in the view // intersect the given screen x, y coordinates view.hitTest(event) .then(getGraphics); });view.on("click", function(event) { // you must overwrite default click-for-popup // behavior to display your own popup event.stopPropagation(); // Get the coordinates of the click on the view var lat = Math.round(event.mapPoint.latitude * 1000) / 1000; var lon = Math.round(event.mapPoint.longitude * 1000) / 1000; view.popup.open({ // Set the popup's title to the coordinates of the location title: "Reverse geocode: [" + lon + ", " + lat + "]", location: event.mapPoint // Set the location of the popup to the clicked location content: "This is a point of interest" // content displayed in the popup }); });
- double-clickinherited
Fires after double-clicking on the view.
- Properties:
- mapPoint Point
The point location of the click on the view in the spatial reference of the map.
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the click on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the click on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates the current mouse button state.
Value Description 0 left click (or touch) 1 middle click 2 right click type StringFor double-click the type is always
double-click.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
Example:view.on("double-click", function(event) { // The event object contains the mapPoint and the screen coordinates of the location // that was clicked. console.log("screen point", event.x, event.y); console.log("map point", event.mapPoint); });
- draginherited
Fires during a pointer drag on the view.
- Properties:
- action String
Indicates the state of the drag. The two values
addedandremovedindicate a change in the number of pointers involved.Possible Values: start | added | update | removed | end
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
origin ObjectScreen coordinates of the start of the drag.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked at the start of the drag. See MouseEvent.button.
Value Description 0 left mouse button (or touch) 1 middle mouse button 2 right mouse button buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringFor drag the type is always
drag.radius NumberThe radius of a sphere around the multiple pointers involved in this drag. Or 0 while only a single pointer is used.
angle NumberAmount of rotation (in degrees) since the last event of type
start.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM MouseEvent.
Example:view.on("drag", function(evt){ // Print out the current state of the // drag event. console.log("drag state", evt.action); });
- focusinheritedSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Fires when browser focus is on the view.
- Properties:
- target View
The view that the browser focus is currently on.
native ObjectA standard DOM KeyboardEvent.
- holdinherited
Fires after holding either a mouse button or a single finger on the view for a short amount of time.
- Properties:
- mapPoint Point
The point location of the click on the view in the spatial reference of the map.
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the hold on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the hold on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was held down. See MouseEvent.button.
Value Description 0 left mouse button (or touch) 1 middle mouse button 2 right mouse button buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringFor hold the type is always
hold.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
Example:view.on("hold", function(event) { // The event object contains the mapPoint and the screen coordinates of the location // that was clicked. console.log("hold at screen point", event.x, event.y); console.log("hold at map point", event.mapPoint); });
- immediate-clickinheritedSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.7
Fires right after a user clicks on the view. In contrast to the click event, the immediate-click event is emitted as soon as the user clicks on the view, and is not inhibited by a double-click event. This event is useful for interactive experiences that require feedback without delay.
- Properties:
- mapPoint Point
The point location of the click on the view in the spatial reference of the map.
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the click on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the click on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked. See MouseEvent.button.
Value Description 0 left click (or touch) 1 middle click 2 right click buttons NumberIndicates which buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringFor click the type is always
immediate-click.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
Example:// Set up an immediate-click event handler and retrieve the screen point view.on("immediate-click", function(event) { // the hitTest() checks to see if any graphics in the view // intersect the given screen x, y coordinates view.hitTest(event) .then(getGraphics); });
- key-downinherited
Fires after a keyboard key is pressed.
- Properties:
- repeat Boolean
Indicates whether this is the first event emitted due to the key press, or a repeat.
key StringThe key value that was pressed, according to the MDN full list of key values.
type StringFor key-down the type is always
key-down.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM KeyboardEvent.
Example:// Zoom in when user clicks on "a" button // Zoom out when user clicks on "s" button view.on("key-down", function(evt){ console.log("key-down", evt); if (evt.key === "a"){ var zm = view.zoom + 1; view.goTo({ target: view.center, zoom: zm }); } else if(evt.key == "s"){ var zm = view.zoom - 1; view.goTo({ target: view.center, zoom: zm }); } });
- key-upinherited
Fires after a keyboard key is released.
- Properties:
- type String
For key-up the type is always
key-up.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM KeyboardEvent.
- layerview-createinherited
Fires after each layer in the map has a corresponding LayerView created and rendered in the view.
- Properties:
- layer Layer
The layer in the map for which the
layerViewwas created.layerView LayerViewThe LayerView rendered in the view representing the layer in
layer. - See also:
Example:// This function fires each time a layer view is created for a layer in // the map of the view. view.on("layerview-create", function(event) { // The event contains the layer and its layer view that has just been // created. Here we check for the creation of a layer view for a layer with // a specific id, and log the layer view if (event.layer.id === "satellite") { // The LayerView for the desired layer console.log(event.layerView); } });
- layerview-destroyinherited
Fires after a LayerView is destroyed and is no longer rendered in the view. This happens for example when a layer is removed from the map of the view.
- mouse-wheelinherited
Fires when a wheel button of a pointing device (typically a mouse) is scrolled on the view.
- Properties:
- x Number
The horizontal screen coordinate of the click on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the click on the view.
deltaY NumberNumber representing the vertical scroll amount.
type StringFor mouse-wheel the type is always
mouse-wheel.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM WheelEvent.
Example:view.on("mouse-wheel", function(evt){ // deltaY value is postive when wheel is scrolled up // and it is negative when wheel is scrolled down. console.log(evt.deltaY); });
- pointer-downinherited
Fires after a mouse button is pressed, or a finger touches the display.
- Properties:
- pointerId Number
Uniquely identifies a pointer between multiple down, move, and up events. Ids might get reused after a pointer-up event.
pointerType StringIndicates the pointer type.
Possible Values: mouse | touch
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringFor pointer-down the type is always
pointer-down.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents event propagation bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was emitted.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
- pointer-enterinherited
Fires after a mouse cursor enters the view, or a display touch begins.
- Properties:
- pointerId Number
Uniquely identifies a pointer between multiple events. Ids might get reused after a pointer-up event.
pointerType StringIndicates the pointer type.
Possible Values: mouse | touch
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringType of the event. It is always
pointer-enterfor this event.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents further propagation of the current event bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was created.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
- pointer-leaveinherited
Fires after a mouse cursor leaves the view, or a display touch ends.
- Properties:
- pointerId Number
Uniquely identifies a pointer between multiple events. Ids might get reused after a pointer-up event.
pointerType StringIndicates the pointer type.
Possible Values: mouse | touch
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringType of the event. It is always
pointer-leavefor this event.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents further propagation of the current event bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was created.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
- pointer-moveinherited
Fires after the mouse or a finger on the display moves.
- Properties:
- pointerId Number
Uniquely identifies a pointer between multiple down, move, and up events. Ids might get reused after a pointer-up event.
pointerType StringIndicates the pointer type.
Possible Values: mouse | touch
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringType of the event. It is always
pointer-movefor this event.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents further propagation of the current event bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was created.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.
Example:// Fires `pointer-move` event when user clicks on "Shift" // key and moves the pointer on the view. view.on('pointer-move', ["Shift"], function(evt){ var point = view2d.toMap({x: evt.x, y: evt.y}); bufferPoint(point); });
- pointer-upinherited
Fires after a mouse button is released, or a display touch ends.
- Properties:
- pointerId Number
Uniquely identifies a pointer between multiple down, move, and up events. Ids might get reused after a pointer-up event.
pointerType StringIndicates the pointer type.
Possible Values: mouse | touch
x NumberThe horizontal screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
y NumberThe vertical screen coordinate of the pointer on the view.
button NumberIndicates which mouse button was clicked.
buttons NumberIndicates which mouse buttons are pressed when the event is triggered. See MouseEvent.buttons.
type StringType of the event. It is always
pointer-upfor this event.stopPropagation FunctionPrevents further propagation of the current event bubbling up the event chain.
timestamp NumberTime stamp (in milliseconds) at which the event was created.
native ObjectA standard DOM PointerEvent.